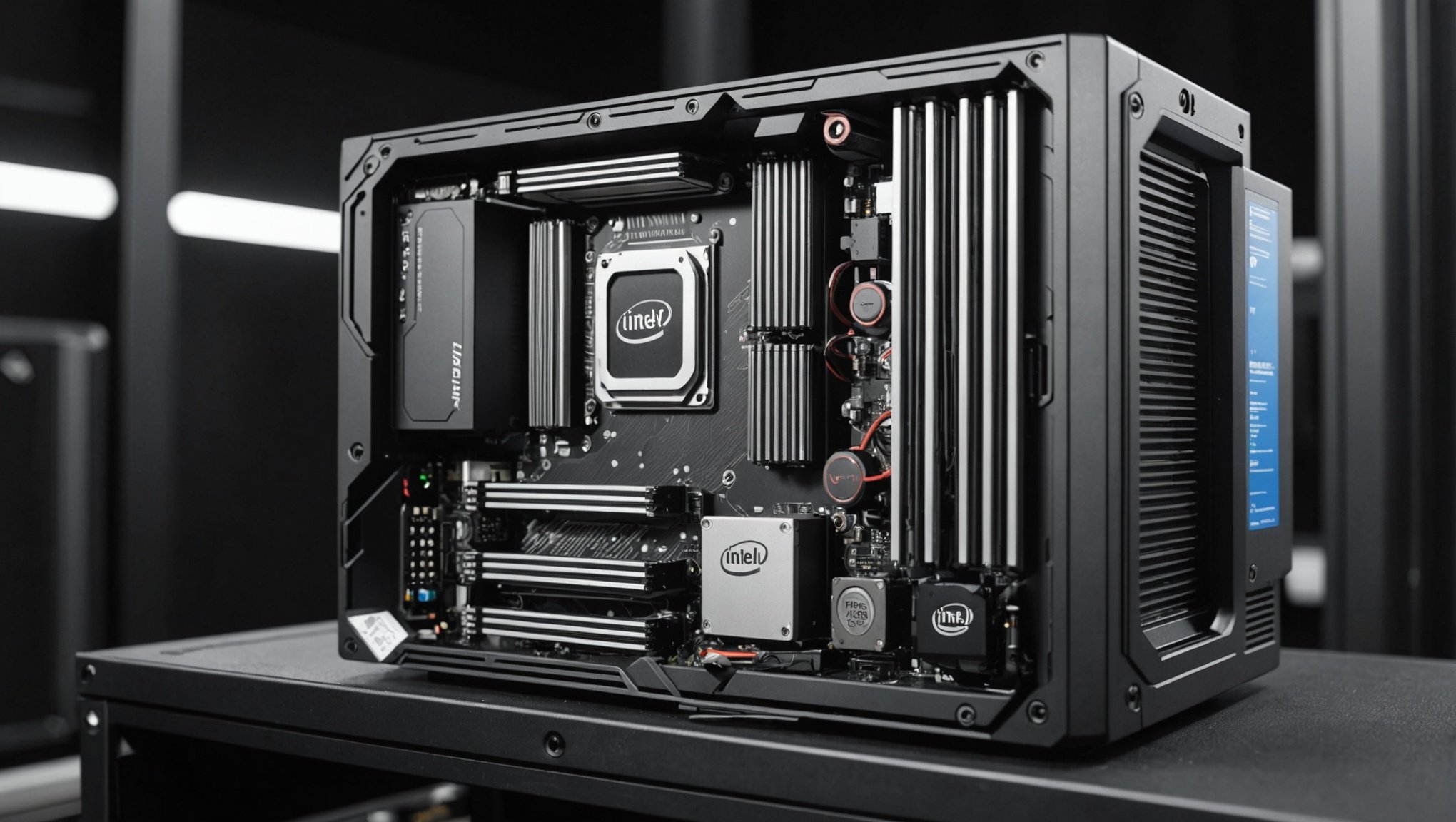
Compact SFF cases offer unique advantages but can pose significant challenges for airflow and cooling, especially with high-performance processors like the Intel Core i7-10700K. Efficient cooling is essential to maintain performance and longevity. This guide explores expert tips and strategies that will help you optimize airflow, reduce thermal throttling, and ensure your powerful setup runs smoothly. Whether you're building a new rig or upgrading, mastering these techniques will enhance your gaming or productivity experience.
Understanding Airflow Dynamics in SFF Cases
In the realm of SFF cases, airflow dynamics play a pivotal role in ensuring effective thermal management. The compact nature of these cases makes it imperative to understand how airflow can be optimised to prevent overheating.
Have you seen this : Maximize Your 4K Streaming Experience: Optimal Ways to Connect Your QNAP TS-451+ NAS with Plex Media Server
Airflow in these small form factor cases is critical due to the limited space, which can restrict the movement of air. Effective airflow dynamics help in maintaining optimal temperatures, ensuring that components perform efficiently and have a longer lifespan. The tight confines mean that every bit of airflow needs to be strategically managed to avoid hotspots.
Air pressure within these cases significantly impacts cooling efficiency. Positive air pressure, where more air is being pushed into the case than being extracted, can help in reducing dust accumulation and improving cooling. Conversely, negative air pressure can lead to dust build-up but might enhance cooling by drawing more air out. Balancing these pressures is crucial for efficient thermal management.
This might interest you : Maximizing Airflow: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhancing the Cooling System of Your Corsair Crystal Series 680X for Dual GPU Configurations
Key components, such as fans and heat sinks, dictate airflow direction. Their placement and orientation determine how effectively air moves across the components that generate the most heat. Proper alignment ensures that cool air is directed towards critical areas while hot air is expelled efficiently. Understanding these dynamics allows for better customisation and optimisation of cooling solutions in SFF cases.
Choosing the Right Cooling Solutions
Selecting the appropriate cooling solutions for SFF cases involves weighing the pros and cons of air coolers versus liquid coolers. Each has its unique benefits and challenges, especially in compact environments.
Air coolers are often favoured for their simplicity and reliability. They consist of a heat sink and fan, which work together to dissipate heat. In SFF cases, choosing a low-profile air cooler ensures compatibility with limited space. However, they might not provide the same level of cooling efficiency as liquid coolers, especially for high-performance CPUs like the Intel Core i7-10700K.
Liquid coolers, on the other hand, offer superior cooling performance and can handle higher thermal loads. They use a pump to circulate coolant through a loop, transferring heat away from the CPU. While they are more efficient, their installation can be complex, and not all SFF cases can accommodate them due to space constraints.
When considering SFF compatibility, it's crucial to evaluate factors such as the cooler's dimensions, the case's internal layout, and the thermal design power (TDP) of the CPU. Ensuring that the cooling solution fits and functions effectively within the compact space is key to maintaining optimal performance.
Strategic Component Placement
Proper component placement is crucial for enhancing thermal performance and ensuring effective airflow optimisation in SFF cases. Given the limited space, strategic positioning of components is essential to prevent overheating and maintain system efficiency.
Best Practices for Arranging Components: In SFF cases, every millimetre counts. Positioning the CPU and GPU to maximise airflow pathways is vital. Components should be arranged to allow unobstructed air movement, reducing the risk of thermal bottlenecks. Aligning the motherboard in a way that facilitates direct airflow to the CPU can significantly improve cooling efficiency.
Effects of Cable Management on Airflow: Cables can obstruct airflow if not managed properly. Tidy cable management not only improves aesthetics but also enhances airflow by reducing blockages. Using cable ties and routing cables along the case's edges can help maintain a clear path for air, thus improving overall thermal performance.
Utilising Space Effectively: Space in SFF cases is at a premium, so it's important to use it wisely. Installing components like SSDs behind the motherboard tray or opting for M.2 drives instead of traditional HDDs can free up space. This allows for better airflow and cooling, as more room is available for air circulation. Proper space utilisation leads to a cooler, more efficient system.
Implementing Effective Ventilation
In small form factor (SFF) cases, employing the right ventilation strategies is crucial for maintaining efficient thermal management. The compact design necessitates a well-thought-out approach to both fan placement and exhaust flow.
Importance of Intake and Exhaust Fans
To achieve optimal cooling, it's essential to balance intake and exhaust fans. Intake fans draw cool air into the case, while exhaust fans push hot air out. This balance ensures a continuous flow of air, preventing heat build-up. In SFF cases, where space is limited, every fan must be strategically placed to maximise airflow.
Ideal Fan Configurations for SFF Setups
Choosing the right fan placement is key. Typically, positioning intake fans at the front or bottom and exhaust fans at the top or rear can enhance airflow dynamics. This configuration encourages a natural upward flow of hot air, efficiently expelling it from the case.
Monitoring and Adjusting Fan Speeds for Optimal Performance
Regularly monitoring and adjusting fan speeds is vital for maintaining optimal performance. Using fan controllers or software to adjust speeds according to workload can help maintain a stable temperature. This dynamic adjustment ensures that the system remains cool under varying conditions, prolonging the lifespan of components.
Thermal Paste Application Techniques
In the quest for optimal CPU cooling, the application of thermal paste is a critical step. This substance enhances heat transfer between the CPU and its cooler, ensuring efficient thermal management.
Importance of Thermal Paste in Cooling Efficiency
Thermal paste fills microscopic gaps on the CPU surface, allowing for better heat conduction. Without it, air pockets can form, reducing the effectiveness of the cooling solution. Proper application can significantly improve cooling efficiency, leading to better performance and longevity of components.
Step-by-Step Guide on Proper Application
-
Clean the Surface: Before applying new thermal paste, ensure the CPU surface is free from old paste or debris. Use isopropyl alcohol and a soft cloth for cleaning.
-
Apply a Small Amount: A pea-sized dot or a thin line in the centre of the CPU is usually sufficient. This ensures even spreading without excess spillage.
-
Install the Cooler: Place the cooler directly onto the CPU, applying even pressure to distribute the paste uniformly.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Installation
- Over-application: Too much paste can cause spillage and potentially damage other components.
- Uneven Spread: Avoid spreading the paste with fingers or tools, as this can introduce air bubbles, hindering performance.
Monitoring System Temperatures
Effective temperature monitoring is crucial for maintaining system health in small form factor (SFF) cases. Utilizing reliable software tools can help track and manage thermal performance, preventing potential overheating issues.
Recommended Software for Temperature Monitoring
Several software tools are available for monitoring system temperatures. Tools like HWMonitor, Core Temp, and NZXT CAM provide real-time data on CPU and GPU temperatures, fan speeds, and voltage levels. These programs are user-friendly and offer detailed insights into your system’s thermal status, allowing for proactive management of cooling solutions.
Understanding Thermal Thresholds for Intel Core i7-10700K
The Intel Core i7-10700K has a maximum operating temperature, known as the TjMax, of approximately 100°C. It's essential to keep the CPU well below this threshold to avoid thermal throttling and ensure longevity. Ideally, maintaining temperatures below 85°C under load is advisable for optimal performance.
How to Interpret Temperature Readings
Interpreting temperature readings involves understanding what constitutes normal and high temperatures for your components. Regularly monitoring and comparing these readings against manufacturer guidelines helps assess system health. If temperatures frequently approach or exceed safe limits, consider adjusting cooling strategies or enhancing airflow to mitigate risks. Proper interpretation ensures your system remains efficient and reliable.
Troubleshooting Common Cooling Issues
In the compact world of SFF cases, encountering cooling issues can be a frequent challenge. Recognising these problems early is crucial for maintaining system performance.
Identifying Signs of Inadequate Cooling
Signs of inadequate cooling include sudden system shutdowns, frequent thermal throttling, and unusually high temperatures. If your components are overheating, it may lead to reduced performance or even hardware damage. Monitoring these signs is the first step in effective troubleshooting.
Common Problems with SFF Cases and Solutions
SFF challenges often stem from limited airflow. Dust accumulation and poor component placement can exacerbate cooling issues. To address these, ensure regular cleaning and strategic component arrangement. Consider repositioning fans or upgrading to more efficient models to improve airflow.
- Blocked Air Vents: Ensure vents are clear of obstructions.
- Insufficient Fans: Add or reposition fans to enhance airflow.
- Inadequate Thermal Paste: Reapply thermal paste if necessary.
When to Consider Upgrading Cooling Components
If troubleshooting tips do not resolve the issues, it might be time to upgrade your cooling components. High-performance air or liquid coolers can offer better thermal management. Evaluate your system's needs and the available space within your SFF case to choose the most suitable upgrade.
Real-World Experiences and Case Studies
Exploring real-world user experiences with SFF builds provides invaluable insights into effective airflow and cooling strategies. These case studies demonstrate practical applications and highlight lessons learned from different setups.
Successful SFF Builds with Intel Core i7-10700K
Several SFF builds featuring the Intel Core i7-10700K have showcased impressive thermal management. Users have reported achieving optimal temperatures by carefully selecting cooling solutions and strategically placing components. These builds often utilise a combination of low-profile air coolers and efficient cable management to maximise airflow.
User Testimonials on Airflow and Cooling Performance
Enthusiasts frequently share their experiences, emphasising the importance of balancing intake and exhaust fans. One user noted that positioning intake fans at the bottom and exhaust fans at the top significantly improved airflow, keeping the system cool even under heavy loads. Another testimonial highlighted the benefits of using high-quality thermal paste for better heat conduction.
Lessons Learned from Various SFF Setups
From these case studies, several key lessons emerge. Proper component placement and effective cable management are crucial for maintaining efficient airflow. Additionally, regular monitoring of system temperatures helps identify potential issues early, allowing for timely adjustments. These experiences underscore the importance of thoughtful design and ongoing maintenance in achieving successful SFF builds.
Future Trends in SFF Cooling Solutions
As the demand for small form factor (SFF) cases continues to grow, so does the innovation in cooling technology. Future trends indicate a shift towards more efficient and compact solutions to accommodate the unique challenges posed by SFF designs.
Emerging Technologies in Cooling Solutions
Cooling technology is advancing with the development of more efficient heat dissipation methods, such as vapor chamber coolers and advanced liquid cooling systems. These technologies promise to enhance thermal performance without increasing the size of the cooling components, making them ideal for SFF applications.
Predictions for the Future of SFF Case Designs
The future of SFF case designs is likely to see more modular and customizable options, allowing users to tailor their cooling setups to specific needs. Innovations in materials, such as graphene, could also play a role in improving heat conductivity and overall cooling efficiency.
The Role of Community Feedback in Product Development
Community feedback is increasingly vital in shaping the development of new cooling solutions. Manufacturers are leveraging insights from users to refine designs and address common challenges. This collaborative approach ensures that future products are better aligned with user needs, leading to more effective and user-friendly cooling solutions in the SFF market.